
Conjugated anti-HRP may be used to convert an HRP conjugate into a different signal. Jackson ImmunoResearch also offers affinity-purified anti-horseradish peroxidase which may be used to detect HRP or to enhance signal by binding to HRP-conjugated molecules. In addition, secondary antibodies conjugated with fluorescent dyes, including far-red and infrared-emitting dyes, are available for multicolor imaging in modern readers. JIR offers antibodies and streptavidin conjugated with horseradish peroxidase (HRP), alkaline phosphatase and Biotin-SP for use in traditional blots developed with chromogenic or chemiluminescent (ECL) substrates. Towbin et al in 1979 ( Towbin, Staehelin, & Gordon. It is built on a technique that involves transferring, also known as blotting, proteins separated by electrophoresis from the gel to a membrane where they can be visualized specifically. Jackson ImmunoResearch produces the largest diversity of species specific secondary antibody conjugates for use in Western blotting. Western Blot (WB) is a common method to detect and analyze proteins. The reporter fluorescent dye is excited by its characteristic wavelength light, and resulting emitted light is captured by a digital imager. Electrophoretic as well as non-electrophoretic transfer of proteins to membranes was first described in 1979. This process involves the transfer of protein patterns from gel to microporous membrane. When performing a Western blot, the samples used need to be complex biological samples, preferably homogenates of the tissue or tissues of interest.
#Purpose of western blot analysis full#
The reporter enzyme conjugate catalyzes a reaction which converts the chemiluminescent substrate to a light emitting form, and the emitted light is detected by X-ray film or CCD camera.Ĭ. The paper 'Steps of the Western Blot Analysis' discusses a technique that can be used for identifying certain proteins or antibodies in which proteins become separated by the use of electrophoresis, then become transferred to nitrocellulose, and finally reacted with antibodies Download full paper File format. Western blotting is an important procedure for the immunodetection of proteins, particularly proteins that are of low abundance. The Western blot is the test most commonly used to evaluate the biochemical specificity of an antibody to the immunogen used to raise that antibody. The reporter enzyme conjugate catalyzes the conversion of a chromogenic substrate to a colored insoluble precipitate, visible by eye on the blotting membrane.ī.
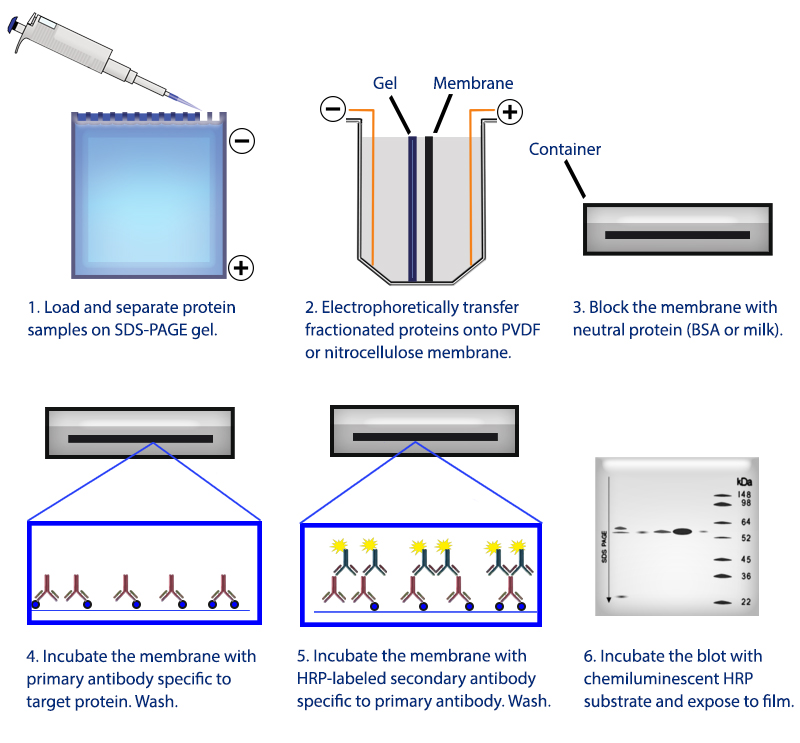
This mixture can include all of the proteins associated with a particular tissue.

The Western blot test separates the blood. A western blot is a laboratory method used to detect specific protein molecules from among a mixture of proteins. The 3 detection methods for Western blot: (A) Colorimetric, (B) Chemiluminescent, and (C) Fluorescent Ī. During the test, a small sample of blood is taken and it is used to detect HIV antibodies, not the HIV virus itself. Read our article about fluorescent western blotting Read more about fluorescent dyes


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
